

Typically, we Indians breeze through life thinking we are above all ailments. The fatty foods we consume and the lack of proper exercise puts us at very high risk for various diseases. The added stress only shortens the time between a healthy youth and crossing over to being ill.
Most people go through life unaware of their conditions and realize something is wrong only when an incident triggers a certain complication. It could be more serious, and these checks can avert being rushed to the emergency room.
People have often shrugged off mild heart attack symptoms especially if they are the silent kind. While normally you would get all the warning signals in the event of a heart attack but if you are diabetic these alarm bells may not go off. The reason for it is that your nerves are affected/damaged by Diabetes and often the symptoms might be mild or negligent.
But let us first tell you about Diabetes and how it can lead to Heart Diseases. To understand it let us start with.
Diabetes is a metabolic disease that occurs when blood sugar or glucose levels are high. The food we consume is turned into glucose or sugar when we eat it, and this is one of our main sources of energy. Our pancreas produces the hormone insulin, which aids in the absorption of glucose from the diet. When the body produces insufficient or no insulin, glucose is retained in the bloodstream, causing blood sugar levels to rise.
It is a condition that manifests itself through subtle symptoms that one should not take for granted. We will discuss the symptoms but first, let us discuss the stage before being Diabetes. It is called being Prediabetic.
Prediabetes is when your sugar levels are higher than normal but not very high enough to be considered as being diabetic.
You may be Prediabetic for years without even realizing it. But if you have any of these risk factors, it is advisable to get yourself tested for Diabetes.
A simple blood test as advised by your physician can reveal if you are Prediabetic. If you find out that you are Prediabetic, do not panic a few simple preventive steps can help you put off being diabetic.
Just make a few adjustments to your lifestyle by following these:
Identifying which Diabetes, you have
But if you are diagnosed as diabetic, check which type of Diabetes you have. For this we shall now explain:
What are types of Diabetes?
The different types of Diabetes are Type 1, Type 2, and Gestational Diabetes.

Generally associated with adolescents and young adults however sometimes can also be developed in adults.
In this type of Diabetes, the body’s autoimmune system which acts as a barrier to infections and gets rid of bacteria, viruses, etc. becomes weak or breaks down. The body starts attacking the pancreas and the beta cells that produce insulin.
This prevents your body from making insulin which is required to convert the glucose from our blood to fuel that our body needs. Without insulin, our bodies do not get the required glucose, which accumulates in the bloodstream, leading to various other health complications.
Type1 diabetic patients are required to take insulin every day. This is why it is known as insulin-dependent Diabetes.
Type 1 Diabetes symptoms in kids
The most common symptoms in kids who might have Type1 Diabetes are:


The causes of Type 1 Diabetes can be:
Being in control of your blood pressure
Being in control of your cholesterol

This type of Diabetes can affect people of any age, though known to mostly on-set in middle age. The beginning is with insulin resistance. The pancreas which produces insulin either produces less insulin or the cells which respond to insulin poorly do not take in enough sugar and thus leaving extra glucose/sugar in the blood. As the capacity of the pancreas to produce insulin diminishes you must depend on oral medication or injected insulin to manage the excess sugar in the blood.
The 5 main symptoms of type 2 Diabetes are:
The diagnosis for Type 1 Diabetes is similar to Type 2 Diabetes.
These are the tests that are recommended to investigate if you have Diabetes in the first place:
In addition to these tests to check for Type 1 Diabetes, Antibody Test is also called for.


During pregnancy, the female body produces hormones that build up insulin resistance. This leads to a condition called gestational Diabetes, which can lead to a risk of developing Type 2 Diabetes a few years after delivery.
Being diabetic can pose a challenge to a person. But certain measures have to be carried out especially when you are out by yourself.
Make sure that people around you for example if you are in school/college or working know your condition so that they know how to respond in case of an emergency.
Make a toolkit to assist you, and include these essentials in it:
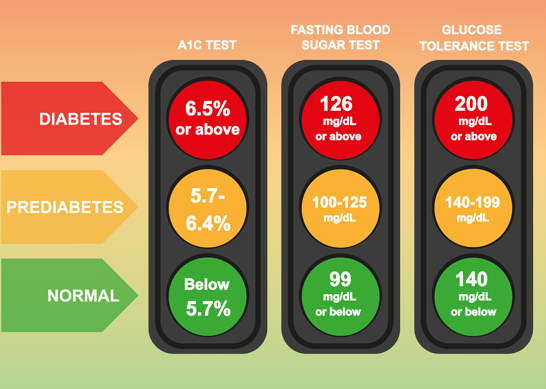
Being alert about your condition helps keep it in control and reduces the risks of any further complications. We recommend that these targets become the highlight and attention of your care plan.
Target Blood Glucose Levels for Diabetics:
https://www.diabetes.org/diabetes/a1c/diagnosis2
HbA1c/A1c – is a test that is also used to give an average blood glucose level over the past three months.
Remember A1C targets can also depend on how long you have had Diabetes and whether or not you have other health problems.
Also, check your cholesterol levels, Target Cholesterol Levels :
Journal of the American College of Cardiology (JACC), 20181
Food
1. Quantity of carbohydrates: We get our energy from three sources of food (carbohydrates, protein, and fat). Out of these carbohydrates affect blood glucose the most. Having a carb-rich diet can affect your blood glucose and will not help in bringing it to the desired levels to maintain a healthy control.

2. Type of carbohydrates: The type of carbohydrate also matters a lot. The higher the glycaemic index of carbs the more tends to spike blood glucose rapidly. Liquid carbs can drastically increase blood glucose as compared to solid carbs.
3. Fats: Consuming fatty foods makes you more insulin resistant.
4. Caffeine: It has been found that while caffeine stimulates the release of adrenaline it also increases insulin resistance.
5. Alcohol: While having alcohol be mindful of the carbohydrate-rich mixers (like juices) as they can spike your blood glucose levels.
6. Dehydration: Being dehydrated can increase your blood glucose.
7. Mealtime: Eating late-night heavy carb-laden dinners can increase your blood glucose at night.
1. Dosage: The dose of medication taken naturally impacts blood glucose.
2. Timing: The timing of the medication oral or insulin injection is critical as well.
1. Light, moderate, or heavy physical exercise: It is found that light exercise like walking is more beneficial. Heavy exercise like weightlifting or sprinting can lead to a sudden drop in blood glucose levels.
2. Time of the day when you work out: Working out in the morning can result in a smaller drop in blood glucose.
3. Food and insulin time: Eating closer to the time of physical activity will show a drop in blood glucose as the food is not yet been absorbed but once the exercise ends and the digestion has restarted the blood glucose levels will rise.
1. Sleep quantity and quality: It has been found that blood glucose levels are directly related to sleep. Not getting enough sleep, or sound sleep can raise blood glucose levels.
2. Stress: The body releases cortisol to combat stress, which is known to increase blood glucose. Keeping stress under control will help keep blood glucose in check.
3. Smoking: It is known to increase insulin resistance which is not good for diabetics.

If you are diabetic either Type 1 or 2 these are some key action points that must be followed:

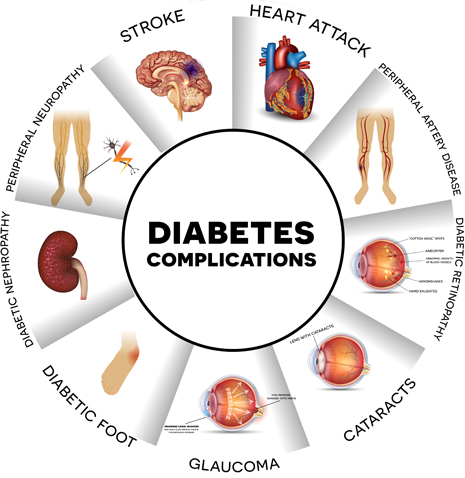
Being diabetic can lead to multiple other health conditions. Developing serious Cardiovascular complications is one of the highest probabilities in diabetics.
Cardiovascular largely means the blood circulation or flow in our bodies. Often when cholesterol builds up it causes plaque to block the arteries. This plaque can also break and will be tried to be repaired by platelets coming to aid it. This may lead to blocking of the blood circulation developing a serious lack of oxygen leading to a heart attack, and a lack of blood to the brain can cause a stroke.
Diabetics develop Heart Diseases earlier than non-diabetics due to various reasons. One of them is high blood glucose leading to blood vessel damage. This in turn raises the threat of Heart Diseases. Long-term high blood sugar in diabetics can also lead to damage to the nerves.
The following conditions paired with Diabetes raise the risk of Heart Disease.
High Blood Pressure or Hypertension: Having a higher than normal blood pressure puts a strain on the heart to pump blood. This can end up damaging the blood vessels leading to a stroke or heart attack.
LDL or bad cholesterol: This can form plaque on artery walls clogging them and leading to Heart Diseases.
High Triglycerides: This is a type of fat that along with the low presence of HDL or good cholesterol can lead to the hardening of arteries.
Smoking: The effects of smoking are similar to Diabetes, narrowing down the blood vessels. Having Diabetes and being a smoker doubles the chances of Heart Disease.
Family History: If somebody in the family has a past history of coronary illness the possibilities of being impacted by coronary illness are higher.
If they have had a Cardiovascular failure before 50 and you have Diabetes, the possibilities of you developing Heart Diseases jump exponentially.
Reference: https://www.diabetesatlas.org/data/en/country/93/in.html
As the instances of Diabetes rise the world over the risks related to CVD or Cardiovascular diseases are substantially rising too. The mortality rate in both genders of diabetics is largely attributed to Cardiovascular diseases due to the presence of stress, increased coagulability, endothelial dysfunction, and autonomic neuropathy.
These are a few risk factors/complications related to Diabetes and Cardiovascular Diseases
The tests that are recommended especially for the hearts of diabetics are:
1. Blood Pressure
With high blood pressure comes a higher risk of heart attack, heart failure, stroke, and renal/kidney failure. It is therefore important that you keep your blood pressure in check by either getting it checked by a physician or using a BP monitor to check your systolic and diastolic pressure.
2. Carotid ultrasound
This helps determine if there is any narrowing of arteries and subsequent blockage in them due to plaque build-up.
3. Computerized tomography (CT) of the heart and calcium scores:
Helps in checking if there are calcium deposits in the heart and arteries leading to heart trouble.
4. Electrocardiogram (ECG) a test that finds out if
5. Ambulatory electrocardiogram (Holter monitor)
A test that measures, while you are doing your regular mundane activities the electrical activity inside your heart. i> if you are prone to heart attack
6. Echocardiography (echo)
A test that determines how each of the heart chambers is working, the heart’s structure, and the heart’s motion in a graphic way. It additionally shows how wellconstructed the heart muscle is and that the heart is pumping blood to its best limit.
7. Exercise stress test
It is a test that determines safe levels of exercise for you based on a treadmill test that checks how well the heart pumps blood while doing strenuous activities like exercise, while also checking if the arteries are sending enough blood to the heart.
8. Coronary angiography
This test is also known as cardiac catheterization and helps to check for blockages of arteries and their severity.

Symptoms of a typical heart attack are:
Neuropathy or nerve damage in diabetics which is a major cause of tingling in hands and feet is more serious than just that. This can lead to major consequences like silent heart attacks.
How to be alert to nerve damage, look out for these signs:
If you have had a silent heart attack, check for these symptoms
How do diabetics keep their hearts healthy/ Habits that make the Heart Healthy?
Management of Diabetes is one of the key factors to averting Heart Disease if you are diabetic. The aim is not just to keep your blood sugar levels in control but also to work towards reducing the risk of Heart Disease as the two are interlinked.
Here are some tips to remain Heart Healthy.

Managing your Diabetes is a good way of keeping other complications at bay. A healthy lifestyle may help in the prevention of certain diseases and if already affected it will reduce the risks associated with the condition. If you see any prevalent symptoms see your doctor, get the recommended tests done, and do not ignore your health. After all, it is our one true wealth.